Web AR vs App AR: a detailed comparison
Contents
As its name suggests web AR is the ability to consume AR experiences from a web browser on a mobile device: Google Chrome from Android or Safari from iOS. Therefore it is not necessary to download any kind of mobile app to visualize augmented reality experiences. If you want to know more information about this technology in this post we talk more in detail about it.
On the other hand, app-based AR are the set of AR experiences that must be consumed through a specific mobile app. In these cases the user must download an app from an application market (Google Play or App Store) before being able to consume any type of experience.
In this post we will talk about the main differences between the two, trying to highlight the advantages or disadvantages that web AR has over AR for apps.
Main advantages and disadvantages of Web AR vs. App AR
Compatibility, ease of consumption and sharing: KPIs and massive use
In this section, web AR wins by a landslide. The friction of the apps on the one hand, where the user must download a different app for each experience, with the corresponding data consumption, storage on the phone, and the time it takes to even start the AR. And on the other hand, the simplicity of using and launching an AR web experience, through a simple web link or QR code. This means that the potential mass use of augmented reality is necessarily based on AR web experiences. In sectors like retail, marketing, advertising, gamification, tourism and culture, user experience (UX), shopping, e-commerce, etc. Any sector where the goal is to reach a large number of people requires that it is essential to provide an easy, convenient and fast process to access information.
For example, in this experience created by “The Broadway League”, 90% of the people who saw their ads interacted with the AR experience, generating more than 750 hours of interaction and 22% of users who shared the experience. Overall they achieved 4% of direct accesses from the experience to the ticketing page, double the 2% they historically achieved without this type of actions. This is just one more example of the growing trend of AR web usage in our times.
On a compatibility level there was a belief that web AR had many limitations, well this is no longer the case. It is true that today any app is available in the two main markets of Google and Apple. It is also true that practically any app that makes use of libraries or augmented reality functions can reach any phone of a certain range (medium/high). But the same is true for AR experiences on the web, where compatibility is close to 93% of the browsers installed on phones. This means that, in this situation, what makes the difference is the way in which an experience can be consumed and shared, and thus ensure that its use is widespread.
Technical differences: ARKit and ARCore not on the web. For how long?
The main advantage of AR for apps over the web is the native libraries that Google and Apple have been developing over the years for Android and iOS respectively: ARCore and ARKit. These libraries offer a series of very powerful functionalities, such as positioning any AR content in space, and being able to track on all axes, keeping the content anchored. What is important to know is that both Android and iOS are developing the web adaptation of these libraries, which is known as web XR. In fact Android already has it published in its version of Chrome (already available on Onirix), so accessing this type of complex functionality is already a reality for the web part. In iOS we may still have to wait to have it available in Safari, but many companies (including Onirix) are already developing their own library of functionality for AR on surfaces, and thus make up for the lack of access to web XR from iOS. Having the full power of ARKit in Safari will only be a matter of time.
Cost of creation: professional profiles, time spent.
Another really important aspect in favor of web AR is the cost of creating and customizing experiences. This cost can be measured in terms of the expertise of the staff required, as well as the time spent to generate a successful experience. Being a web technology, there is an infinitely greater number of professionals who have the knowledge to design and develop web experiences, rather than more specific, and increasingly scarce, professionals who have experience in the design and development of mobile apps.
In addition, getting started in the web world, in all its forms, is much easier. There is much more documentation for working with HTML, CSS or JavaScript than there may be for programming in Swift (programming language for iOS).
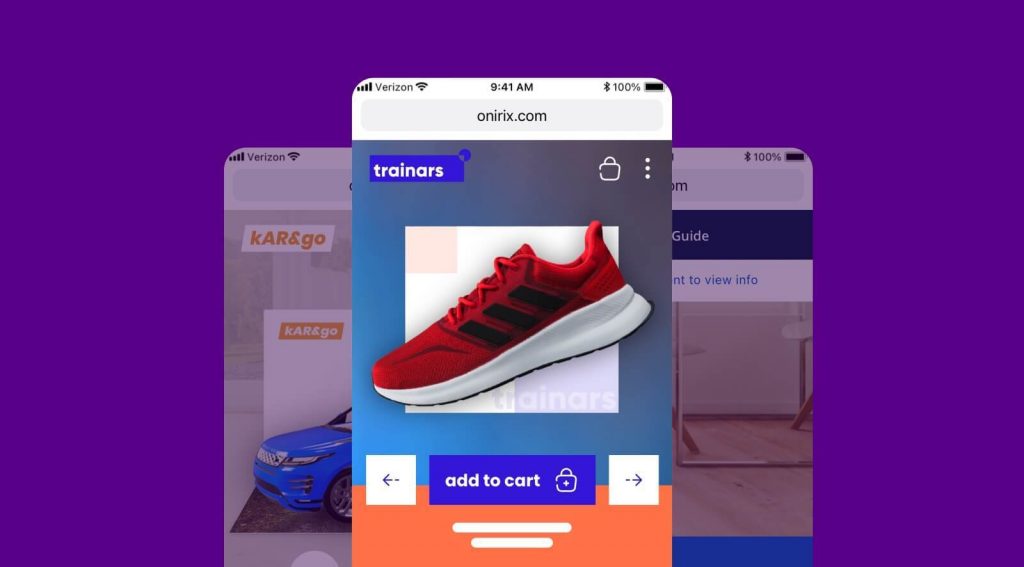

With tools like Onirix, and starting from existing templates, such as the experience library, it is really easy to start shaping complex and professional experiences that an end customer may need to bring to market.
Experiences that before could take more than 50 or 100 hours of development, can be tested in minutes, and adapted to the client’s needs in a few hours. Saving time and personnel is key, and the ability to validate an idea in an agile way is even more so.
Problems with validating and updating apps in application markets
Here again, web AR is a much more attractive technology, as it does not require any validation from Apple or Google for immediate updating. If you want to include a change in a web experience, it is a matter of minutes to include it in production and publish it. However, if we need to do the same with an app, a more complex process is required in the development phase (compilation and deployment), and in the publishing phase (going through the validation filter of the app markets). The difference in this case can be from minutes to several days.
In addition, the initial validation process of an app, in the specific case of Apple, can be a real pain for developers and project managers. It is essential that they take these times into account in their planning, and that they also take into account the client’s requirements well in advance, since the list of restrictions imposed by Apple to be part of its App Store is quite extensive.
Measurement and analytical capabilities
Similarly, being a web experience, web AR allows you to inject components such as Google analytics in a simple way, and with respect to the previous point, add events at any time, and thus allow a successful measurement, almost in real time. In the same way as with the validation process, measuring and reporting usage statistics in an app is a much more cumbersome, costly and error-prone process. And there’s no point in making great experiences if we can’t conveniently measure their results and impact on the end user. What our customers want is to be able to evaluate the success of their actions, whether in marketing or in a production line installation process. Optimization is everything in today’s world, and technology has to provide that measurement and optimization.
Conclusions
Augmented reality is one of those technologies that will change the way we interact with our environment. That is why the main companies are betting heavily on it. In the same way, they know that the market depends on AR being easy to consume, to use and to share, and that is why the AR web is that point on the road, where we are already.
There are many beliefs about the limitations of web AR that we try to break down here. The web option is better than the app option in all aspects, and although it has some specific technological limitations, they are already being addressed and solved with the development of the web XR. That is why we at Onirix bet on web-based AR, because in essence it can solve the problem of any customer in a simpler and much less costly way.

